In NS Module 3, we examined how the security properties of confidentiality and data integrity could be protected by using symmetric key cryptography and signed message digests. In this lab exercise, you will learn how to write a program that makes use of 3DES for data encryption, SHA256 for creating message digests and RSA for digital signing.
At the end of this lab exercise, you should be able to:
- Understand how symmetric key cryptography can be used to encrypt data and protect its confidentiality.
- Understand how multiple blocks of data are handled using different block cipher modes and padding.
- Compare the different block cipher modes in terms of how they operate.
- Understand how hash functions can be used to create fixed-length message digests.
- Understand how public key cryptography (e.g., RSA algorithm) can be used to create digital signatures.
- Understand how to create message digest using hash functions (e.g., MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, SHA-512, etc) and sign it using RSA to guarantee data integrity.
There are 3 parts of this lab:
- Symmetric key encryption for a text file
- Symmetric key encryption for an image file
- Signed message digests
System Requirements
The starter code provided to you is written in Python. You need at least Python 3.10 to complete this assignment and the cryptography module. We will use the Python cryptography module to write our program instead of implementing 3DES, RSA and SHA-256 directly. You will also need this module for your Programming Assignment 2, so take this lab as a precursor to the asssignment.
While you can develop in Python using any OS, this lab is tested to run on a POSIX-compliant OS (path, etc is resolved) so it is not guaranteed that it will run on other OS. You need to fix OS-specific problems in the starter code by yourself.
Starter Code
Download the starter code:
git clone https://github.com/natalieagus/nslab2.git
This will result in a directory with the following structure:
nslab2
|-original_files
|-longtext.txt
|-shorttext.txt
|-SUTD.bmp
|-triangle.bmp
|-.gitignore
|-1_encrypt_text.py
|-2_encrypt_image.py
|-3_sign_digest.py
|-README.md
|-requirements.txt
Then, cd to nslab2 and install the required modules:
python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt
In this lab, you’re only required to modify all the 3 python files. You don’t need to submit your code, and simply answer the questionnaire on eDimension as usual. There are areas labeled in these .py files as TODO, and these are your tasks.
Test the Starter Code
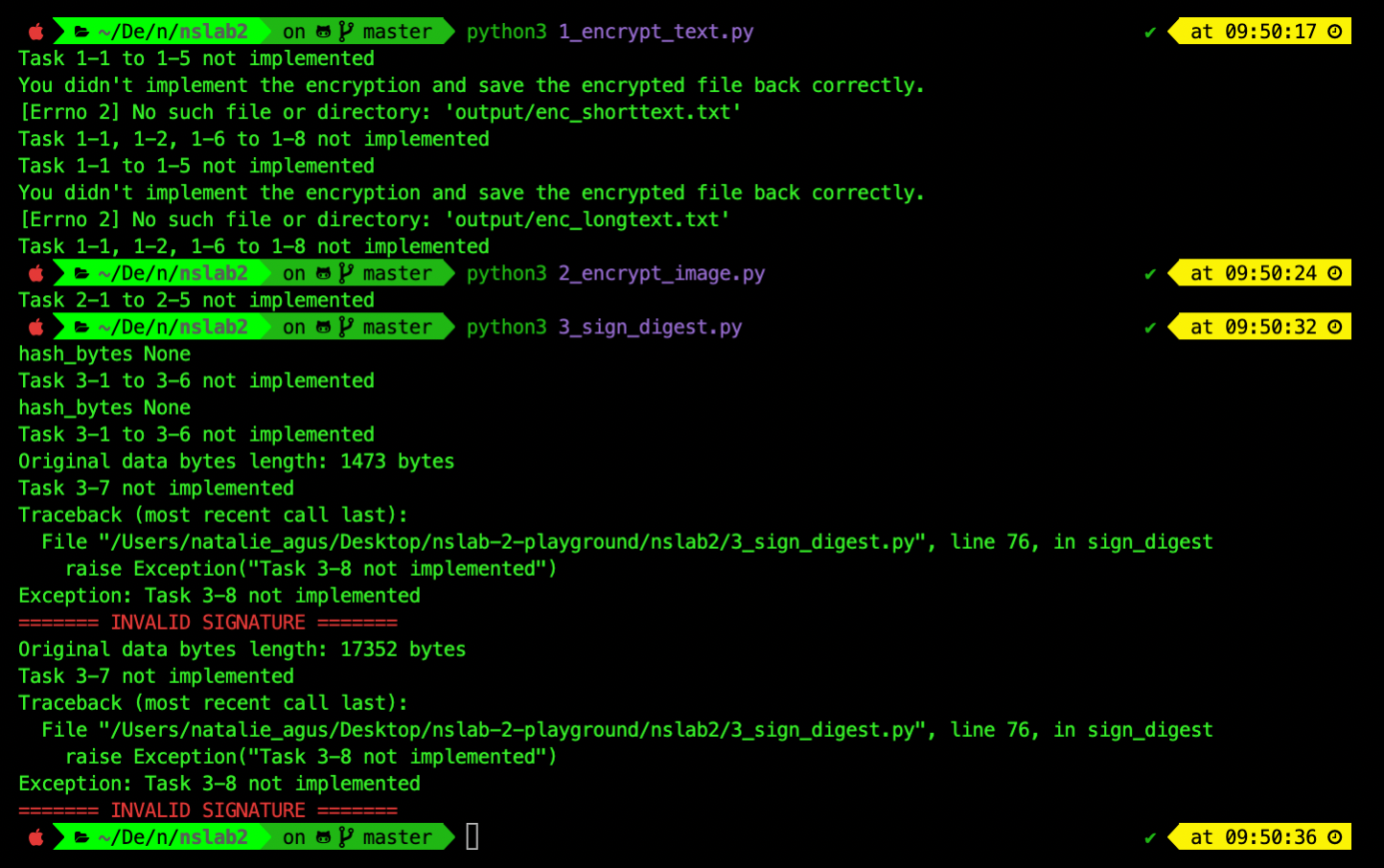
Running the three .py files at this point should give you the following printouts stating that you havent implemented the relevant tasks:
Debug Notes
Invalid Syntax
Some of you might encounter the error when running python3 [starter-code].py
match convert_bytes_to_int(read_bytes(client_socket, 8)):
^
case 0:
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
That’s because your python3 is NOT aliased to python3.10 or that you don’t have python3.10 installed. Fix this on your own. You’re a CS major student. Not knowing how to install Python and manage its libraries is a really really bad thing; it’s like as if the entire 50.002 and the first 6 weeks of CSE doesn’t mean anything to you.
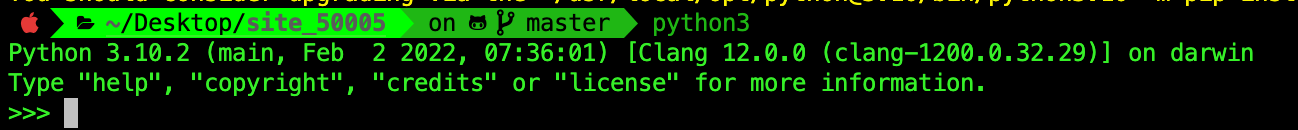
In this handout, we assume that python3 is always aliased to python3.10.
That is, if you type python3 in the terminal, you’ll see at least version 3.10 printed out:
Module Not Found
Some of you might encouter the error ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘cryptography’. You should know what you need to do by now as a CS student. If you have installed cryptography using pip install cryptography, but still suffer from this error, it simply means that the pip you used does not install to the path library of whatever python3 version you are using right now. That is, you may have mixed up Python and pip versions on your machine.
Assuming your python3 is aliased to python3.10, then you can do the following as stated above, instead of pip3 install -r requirements.txt you copy pasted from somewhere.
python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt